Should You Repair A 20 Year Old Refrigerator

Nutrient in a refrigerator with its door open

A refrigerator (fridge) is a commercial and home apparatus consisting of a thermally insulated compartment and a oestrus pump (mechanical, electronic or chemical) that transfers heat from its inside to its external environment so that its inside is cooled to a temperature beneath the room temperature. Refrigeration is an essential food storage technique around the world. The lower temperature lowers the reproduction rate of leaner, then the refrigerator reduces the rate of spoilage. A refrigerator maintains a temperature a few degrees above the freezing point of water. The optimal temperature range for perishable nutrient storage is 3 to 5 °C (37 to 41 °F).[1] A like device that maintains a temperature beneath the freezing indicate of water is called a freezer. The refrigerator replaced the icebox, which had been a mutual household appliance for nigh a century and a half. The United States Food and Drug Administration recommends that the refrigerator exist kept at or below 4 °C (40 °F) and that the freezer be regulated at −18 °C (0 °F).[2]
The first cooling systems for food involved water ice. Artificial refrigeration began in the mid-1750s, and developed in the early 1800s. In 1834, the first working vapor-pinch refrigeration organization was built. The first commercial ice-making auto was invented in 1854. In 1913, refrigerators for home use were invented. In 1923 Frigidaire introduced the kickoff self-contained unit. The introduction of Freon in the 1920s expanded the fridge market during the 1930s. Home freezers as separate compartments (larger than necessary just for ice cubes) were introduced in 1940. Frozen foods, previously a luxury item, became commonplace.
Freezer units are used in households also every bit in industry and commerce. Commercial refrigerator and freezer units were in utilize for about twoscore years prior to the common home models. The freezer-over-refrigerator style had been the basic style since the 1940s, until modern, side-by-side refrigerators bankrupt the tendency. A vapor compression wheel is used in about household refrigerators, fridge–freezers and freezers. Newer refrigerators may include automatic defrosting, chilled water, and ice from a dispenser in the door.
Domestic refrigerators and freezers for food storage are made in a range of sizes. Among the smallest are Peltier-type refrigerators designed to chill beverages. A large domestic fridge stands as alpine as a person and may be near 1 metre (three ft iii in) broad with a chapters of 0.six grand3 (21 cu ft). Refrigerators and freezers may be free-standing, or built into a kitchen. The refrigerator allows the modernistic household to keep food fresh for longer than earlier. Freezers allow people to buy perishable food in bulk and consume it at leisure, and take bulk purchases.
History [edit]
Technology development [edit]
Ancient origins
Ancient Iranians were among the first to invent a form of big evaporative cooler chosen yakhchāls using subterranean storage spaces, a large domed in a higher place-footing structure made with thick walls and outfitted with wind catchers (called "badgirs"), walled off further into a series of "qanats", or a way of aqueduct used in Ancient Iran.[three] [iv]
Pre-electric refrigeration
In modern times, earlier the invention of the modern electric refrigerator, icehouses and iceboxes were used to provide cool storage for most of the year. Placed near freshwater lakes or packed with snow and water ice during the winter, they were one time very common. Natural ways are still used to cool foods today. On mountainsides, runoff from melting snow is a user-friendly way to cool drinks, and during the winter one can keep milk fresh much longer but by keeping it outdoors. The discussion "refrigeratory" was used at least equally early as the 17th century.[5]
Artificial refrigeration
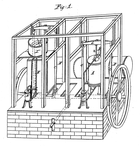
Schematic of Dr. John Gorrie's 1841 mechanical ice automobile

The history of artificial refrigeration began when Scottish professor William Cullen designed a small refrigerating machine in 1755. Cullen used a pump to create a partial vacuum over a container of diethyl ether, which then boiled, absorbing estrus from the surrounding air.[6] The experiment fifty-fifty created a modest amount of ice, but had no practical application at that time.
In 1805, American inventor Oliver Evans described a closed vapor-compression refrigeration cycle for the production of ice by ether under vacuum. In 1820, the British scientist Michael Faraday liquefied ammonia and other gases by using high pressures and low temperatures, and in 1834, an American expatriate in Great Great britain, Jacob Perkins, congenital the first working vapor-compression refrigeration organisation. Information technology was a closed-wheel device that could operate continuously.[7] A similar endeavour was fabricated in 1842, by American physician, John Gorrie,[8] who built a working prototype, just it was a commercial failure. American engineer Alexander Twining took out a British patent in 1850 for a vapor compression system that used ether.
The first practical vapor pinch refrigeration system was built past James Harrison, a Scottish Australian. His 1856 patent was for a vapor pinch system using ether, alcohol or ammonia. He congenital a mechanical ice-making car in 1851 on the banks of the Barwon River at Rocky Point in Geelong, Victoria, and his get-go commercial water ice-making car followed in 1854. Harrison too introduced commercial vapor-pinch refrigeration to breweries and meat packing houses, and past 1861, a dozen of his systems were in operation.
The commencement gas absorption refrigeration system using gaseous ammonia dissolved in h2o (referred to every bit "aqua ammonia") was developed by Ferdinand Carré of French republic in 1859 and patented in 1860. Carl von Linde, an engineering professor at the Technological Academy Munich in Germany, patented an improved method of liquefying gases in 1876. His new process made possible the utilize of gases such as ammonia (NH3), sulfur dioxide (SO2) and methyl chloride (CH3Cl) as refrigerants and they were widely used for that purpose until the late 1920s.[9]
Commercial refrigerators [edit]
Commercial refrigerator and freezer units, which go by many other names, were in use for well-nigh xl years prior to the mutual dwelling house models. They used gas systems such every bit ammonia (R-717) or sulfur dioxide (R-764), which occasionally leaked, making them unsafe for home use. Practical household refrigerators were introduced in 1915 and gained wider acceptance in the United States in the 1930s as prices vicious and non-toxic, non-flammable constructed refrigerants such as Freon-12 (R-12) were introduced. Even so, R-12 damaged the ozone layer, causing governments to result a ban on its use in new refrigerators and air-conditioning systems in 1994. The less harmful replacement for R-12, R-134a (tetrafluoroethane), has been in common use since 1990, but R-12 is still found in many old systems.
A common commercial refrigerator is the glass fronted beverage cooler. These type of appliances are typically designed for specific re-load conditions meaning that they generally have a larger cooling system. This ensures that they are able to cope with a large throughput of drinks and frequent door opening. As a result, information technology is common for these types of commercial refrigerators to have energy consumption of over four kWh per twenty-four hour period.[ citation needed ]Commercial refrigerators efficiency is primarily dependent on the compressor that moves. Refrigerators tin exist able to cause technical harm to the compressor in certain cases.[ clarification needed ] It can be restored or mounted again, depending on the caste of damage. Other kinds of damage, such as a cooler leak, tin go undetected until serious problems arise. Health concerns are chief amidst these issues, with Freon poisoning beingness the most alarming. In order to detect harmful leaks early on, Freon levels demand to exist regularly monitored. Regular routine maintenance should avoid the adventure of keeping nutrient products at the correct temperature. Even the slightest change in circumstances can bear upon consistency, resulting in breaches of food safe and potential penalties.[ opinion ] [ commendation needed ]
Residential refrigerators [edit]

DOMELRE refrigerator c. 1914
In 1913, the first electric refrigerators for habitation and domestic use were invented and produced by Fred West. Wolf of Fort Wayne, Indiana, with models consisting of a unit that was mounted on top of an ice box.[10] [11] His first device, produced over the next few years in several hundred units, was called DOMELRE.[12] [thirteen] In 1914, engineer Nathaniel B. Wales of Detroit, Michigan, introduced an idea for a practical electric refrigeration unit of measurement, which later became the footing for the Kelvinator. A self-contained fridge, with a compressor on the lesser of the cabinet was invented by Alfred Mellowes in 1916. Mellowes produced this refrigerator commercially but was bought out by William C. Durant in 1918, who started the Frigidaire company to mass-produce refrigerators. In 1918, Kelvinator visitor introduced the showtime refrigerator with whatsoever type of automated command. The assimilation fridge was invented by Baltzar von Platen and Carl Munters from Sweden in 1922, while they were still students at the Royal Institute of Technology in Stockholm. It became a worldwide success and was commercialized by Electrolux. Other pioneers included Charles Tellier, David Boyle, and Raoul Pictet. Carl von Linde was the first to patent and make a practical and compact refrigerator.
These home units commonly required the installation of the mechanical parts, motor and compressor, in the basement or an next room while the cold box was located in the kitchen. At that place was a 1922 model that consisted of a wooden common cold box, water-cooled compressor, an water ice cube tray and a 0.25-cubic-metre (9 cu ft) compartment, and cost $714. (A 1922 Model-T Ford cost about $476.) By 1923, Kelvinator held 80 percent of the market for electric refrigerators. Also in 1923 Frigidaire introduced the offset self-independent unit. Nigh this same fourth dimension porcelain-covered metallic cabinets began to appear. Water ice cube trays were introduced more and more during the 1920s; up to this time freezing was not an auxiliary function of the modernistic refrigerator.

General Electric "Monitor-Summit" refrigerator, introduced in 1927, priced at $525, with the first all-steel cabinet, designed by Christian Steenstrup[14]
The get-go refrigerator to see widespread use was the General Electric "Monitor-Top" refrigerator introduced in 1927, then-called, past the public, because of its resemblance to the gun turret on the ironclad warship USS Monitor of the 1860s.[xv] The compressor assembly, which emitted a dandy bargain of heat, was placed above the cabinet, and enclosed by a decorative ring. Over a million units were produced. Equally the refrigerating medium, these refrigerators used either sulfur dioxide, which is corrosive to the eyes and may cause loss of vision, painful skin burns and lesions, or methyl formate, which is highly combustible, harmful to the eyes, and toxic if inhaled or ingested.[16]
The introduction of Freon in the 1920s expanded the refrigerator market during the 1930s and provided a safer, low-toxicity alternative to previously used refrigerants. Separate freezers became common during the 1940s; the term for the unit, popular at the time, was deep freeze. These devices, or appliances, did not get into mass production for use in the dwelling house until after World War II.[17] The 1950s and 1960s saw technical advances like automatic defrosting and automatic ice making. More efficient refrigerators were developed in the 1970s and 1980s, even though ecology issues led to the banning of very effective (Freon) refrigerants. Early fridge models (from 1916) had a cold compartment for ice cube trays. From the late 1920s fresh vegetables were successfully processed through freezing by the Postum Company (the precursor of General Foods), which had acquired the technology when it bought the rights to Clarence Birdseye'south successful fresh freezing methods.
Styles of refrigerators [edit]
In the early 1950s almost refrigerators were white, just from the mid-1950s to the nowadays day, designers and manufacturers take put color onto refrigerators. In the belatedly-1950s/early-1960s, pastel colors like turquoise and pink became popular, and brushed chrome-plating (similar to a stainless steel end) was available on some models. In the tardily 1960s and throughout the 1970s, earth tone colors were popular, including Harvest Gold, Avocado Greenish and almond. In the 1980s, black became stylish. In the tardily 1990s stainless steel came into vogue. Since 1961 the Colour Marketing Grouping has attempted to coordinate the colors of appliances and other consumer goods.
Freezer [edit]
Freezer units are used in households and in industry and commerce. Nutrient stored at or beneath −18 °C (0 °F) is safe indefinitely.[eighteen] Near household freezers maintain temperatures from −23 to −eighteen °C (−9 to 0 °F), although some freezer-merely units can achieve −34 °C (−29 °F) and lower. Fridge freezers more often than not do not achieve lower than −23 °C (−9 °F), since the same coolant loop serves both compartments: Lowering the freezer compartment temperature excessively causes difficulties in maintaining above-freezing temperature in the refrigerator compartment. Domestic freezers can be included equally a separate compartment in a refrigerator, or can be a separate apparatus. Domestic freezers may exist either upright units resembling a fridge, or chests (with the chapeau or door on top, sacrificing convenience for efficiency and partial immunity to power outages).[nineteen] Many modernistic upright freezers come with an ice dispenser built into their door. Some upscale models include thermostat displays and controls, and sometimes flat screen televisions likewise.
Home freezers as separate compartments (larger than necessary but for ice cubes), or as separate units, were introduced in the United States in 1940. Frozen foods, previously a luxury item, became commonplace.
Fridge technologies [edit]

Bones functioning of a refrigerator
Process and components of a conventional refrigerator

Vapor compression cycle – A: hot compartment (kitchen), B: cold compartment (refrigerator box), I: insulation, 1: Condenser, 2: Expansion valve, 3: Evaporator unit, 4: Compressor

An Embraco compressor and fan-assisted condenser coil
Compressor refrigerators [edit]
A vapor compression bicycle is used in most household refrigerators, refrigerator–freezers and freezers. In this cycle, a circulating refrigerant such as R134a enters a compressor equally low-pressure vapor at or slightly below the temperature of the refrigerator interior. The vapor is compressed and exits the compressor as loftier-pressure superheated vapor. The superheated vapor travels under pressure through coils or tubes that make upwardly the condenser; the coils or tubes are passively cooled by exposure to air in the room. The condenser cools the vapor, which liquefies. As the refrigerant leaves the condenser, it is still under pressure but is now only slightly above room temperature. This liquid refrigerant is forced through a metering or throttling device, also known equally an expansion valve (essentially a pivot-pigsty sized constriction in the tubing) to an area of much lower pressure. The sudden subtract in pressure level results in explosive-like flash evaporation of a portion (typically about half) of the liquid. The latent heat absorbed past this flash evaporation is drawn generally from adjacent all the same-liquid refrigerant, a miracle known every bit automobile-refrigeration. This cold and partially vaporized refrigerant continues through the coils or tubes of the evaporator unit of measurement. A fan blows air from the compartment ("box air") beyond these coils or tubes and the refrigerant completely vaporizes, cartoon further latent oestrus from the box air. This cooled air is returned to the refrigerator or freezer compartment, and and so keeps the box air common cold. Note that the cool air in the fridge or freezer is still warmer than the refrigerant in the evaporator. Refrigerant leaves the evaporator, now fully vaporized and slightly heated, and returns to the compressor inlet to continue the cycle.
Mod domestic refrigerators are extremely reliable because motor and compressor are integrated within a welded container, "sealed unit", with greatly reduced likelihood of leakage or contamination. By comparing, externally-coupled refrigeration compressors, such equally those in automobile air conditioning, inevitably leak fluid and lubricant by the shaft seals. This leads to a requirement for periodic recharging and, if ignored, possible compressor failure.
Dual compartment designs [edit]
Refrigerators with two compartments need special design to control the cooling of refrigerator or freezer compartments. Typically, the compressors and condenser coils are mounted at the superlative of the cabinet, with a single fan to cool them both. This organization has a few downsides: each compartment cannot exist controlled independently and the more than humid refrigerator air is mixed with the dry freezer air.[20]
Multiple manufacturers offering dual compressor models. These models accept separate freezer and fridge compartments that operate independently of each other, sometimes mounted inside a unmarried cabinet. Each has its ain separate compressor, condenser and evaporator coils, insulation, thermostat, and door.[ citation needed ]
A hybrid between the two designs is using a separate fan for each compartment, the Dual Fan approach. Doing so allows for split up control and airflow on a single compressor system.[ citation needed ]
Absorption refrigerators [edit]
An absorption refrigerator works differently from a compressor refrigerator, using a source of heat, such as combustion of liquefied petroleum gas, solar thermal energy or an electric heating chemical element. These estrus sources are much quieter than the compressor motor in a typical fridge. A fan or pump might exist the only mechanical moving parts; reliance on convection is considered impractical.
Other uses of an absorption fridge (or "chiller") include large systems used in office buildings or complexes such equally hospitals and universities. These big systems are used to chill a brine solution that is circulated through the edifice.
Peltier upshot refrigerators [edit]
The Peltier effect uses electricity to pump heat directly; refrigerators employing this system are sometimes used for camping, or in situations where noise is non adequate. They can be totally silent (if a fan for air apportionment is not fitted) but are less free energy-efficient than other methods.
Ultra-low temperature refrigerators [edit]
"Ultra-cold" or "ultra-low temperature (ULT)" (typically −fourscore°C or −86°C) freezers, as used for storing biological samples, as well generally employ two stages of cooling, but in cascade. The lower temperature stage uses methyl hydride, or a like gas, as a refrigerant, with its condenser kept at around −forty°C by a second stage which uses a more conventional refrigerant. Well known brands include Forma and Revco (both now Thermo Scientific). For much lower temperatures (around −196°C), laboratories usually buy liquid nitrogen, kept in a Dewar flask, into which the samples are suspended. Cryogenic breast freezers tin can achieve temperatures of downwards to −150°C, and may include a liquid nitrogen backup.
Other refrigerators [edit]
Alternatives to the vapor-compression bike not in current mass production include:
- Acoustic cooling
- Air wheel
- Magnetic cooling
- Malone engine
- Pulse tube
- Stirling cycle
- Thermoelectric cooling
- Thermionic cooling
- Vortex tube
- Water cycle systems.[21]
Architecture [edit]
Many modern refrigerator/freezers have the freezer on top and the refrigerator on the lesser. Nearly refrigerator-freezers—except for manual defrost models or cheaper units—apply what appears to be two thermostats. But the refrigerator compartment is properly temperature controlled. When the refrigerator gets too warm, the thermostat starts the cooling process and a fan circulates the air around the freezer. During this time, the refrigerator also gets colder. The freezer control knob simply controls the amount of air that flows into the refrigerator via a damper arrangement.[22] Changing the fridge temperature will inadvertently modify the freezer temperature in the reverse direction.[ citation needed ] Changing the freezer temperature will have no result on the fridge temperature. The freezer control may as well be adjusted to recoup for whatsoever refrigerator adjustment.[ commendation needed ]
This ways the refrigerator may get also warm. Even so, because only enough air is diverted to the fridge compartment, the freezer usually re-acquires the set temperature quickly, unless the door is opened. When a door is opened, either in the refrigerator or the freezer, the fan in some units stops immediately to forbid excessive frost build up on the freezer's evaporator ringlet, considering this coil is cooling two areas. When the freezer reaches temperature, the unit cycles off, no matter what the fridge temperature is. Modern computerized refrigerators practise not use the damper system. The computer manages fan speed for both compartments, although air is yet blown from the freezer.[ citation needed ]
Features [edit]

The within of a dwelling house refrigerator containing a big variety of everyday nutrient items
Newer refrigerators may include:
- Automated defrosting
- A power failure warning that alerts the user by flashing a temperature display. It may display the maximum temperature reached during the ability failure, and whether frozen nutrient has defrosted or may contain harmful bacteria.
- Chilled water and ice from a dispenser in the door. Water and water ice dispensing became available in the 1970s. In some refrigerators, the process of making water ice is born so the user doesn't have to manually use water ice trays. Some refrigerators accept water chillers and water filtration systems.
- Chiffonier rollers that lets the refrigerator whorl out for easier cleaning
- Adaptable shelves and trays
- A status indicator that notifies when it is time to change the water filter
- An in-door ice caddy, which relocates the ice-maker storage to the freezer door and saves approximately threescore litres (two cu ft) of usable freezer space. It is also removable, and helps to prevent ice-maker clogging.
- A cooling zone in the refrigerator door shelves. Air from the freezer section is diverted to the refrigerator door, to cool milk or juice stored in the door shelf.
- A drop down door congenital into the refrigerator main door, giving easy access to ofttimes used items such every bit milk, thus saving energy by non having to open the main door.
- A Fast Freeze role to rapidly cool foods by running the compressor for a predetermined amount of fourth dimension and thus temporarily lowering the freezer temperature below normal operating levels. It is recommended to apply this characteristic several hours before adding more than 1 kg of unfrozen nutrient to the freezer. For freezers without this feature, lowering the temperature setting to the coldest will have the same effect.
- Freezer Defrost: Early freezer units accumulated ice crystals around the freezing units. This was a result of humidity introduced into the units when the doors to the freezer were opened condensing on the common cold parts, then freezing. This frost buildup required periodic thawing ("defrosting") of the units to maintain their efficiency. Transmission Defrost (referred to as Cyclic) units are however available. Advances in automatic defrosting eliminating the thawing task were introduced in the 1950s, merely are non universal, due to energy performance and cost. These units used a counter that just defrosted the freezer compartment (Freezer Chest) when a specific number of door openings had been made. The units were just a small-scale timer combined with an electrical heater wire that heated the freezer's walls for a short amount of fourth dimension to remove all traces of frost/frosting. Besides, early on units featured freezer compartments located within the larger refrigerator, and accessed past opening the fridge door, and then the smaller internal freezer door; units featuring an entirely separate freezer compartment were introduced in the early 1960s, condign the industry standard by the middle of that decade.
These older freezer compartments were the main cooling body of the refrigerator, and only maintained a temperature of effectually −vi °C (21 °F), which is suitable for keeping food for a week.
- Butter heater: In the early 1950s, the butter conditioner'due south patent was filed and published by the inventor Nave Alfred E. This feature was supposed to "provide a new and improved food storage receptacle for storing butter or the like which may quickly and hands be removed from the refrigerator cabinet for the purpose of cleaning."[23] Considering of the high interest to the invention, companies in Great britain, New Zealand, and Australia started to include the feature into the mass fridge production and soon it became a symbol of the local culture. However, not long after that it was removed from production equally according to the companies this was the simply mode for them to come across new ecology regulations and they plant it inefficient to have a heat generating device inside a commercial fridge.
Later on advances included automatic ice units and self compartmentalized freezing units.
Types of domestic refrigerators [edit]
Domestic refrigerators and freezers for food storage are made in a range of sizes. Amid the smallest is a 4 50 Peltier refrigerator advertised as beingness able to hold 6 cans of beer. A big domestic refrigerator stands as alpine equally a person and may be near one m wide with a chapters of 600 50. Some models for small households fit under kitchen work surfaces, usually most 86 cm high. Refrigerators may be combined with freezers, either stacked with fridge or freezer higher up, below, or next. A refrigerator without a frozen food storage compartment may have a pocket-sized section just to make ice cubes. Freezers may have drawers to store food in, or they may have no divisions (chest freezers).
Refrigerators and freezers may be free-standing, or built into a kitchen.
Three distinct classes of fridge are common:
Compressor refrigerators [edit]
- Compressor refrigerators are by far the nearly common type; they make a noticeable noise, but are most efficient and give greatest cooling effect. Portable compressor refrigerators for recreational vehicle (RV) and camping ground use are expensive just effective and reliable. Refrigeration units for commercial and industrial applications can exist made in diverse sizes, shapes and styles to fit customer needs. Commercial and industrial refrigerators may have their compressors located abroad from the cabinet (similar to divide organization air conditioners) to reduce noise nuisance and reduce the load on air conditioning in hot weather.
Absorption refrigerator [edit]
- Assimilation refrigerators may be used in caravans and trailers, and dwellings lacking electricity, such every bit farms or rural cabins, where they accept a long history. They may be powered by any oestrus source: gas (natural or propane) or kerosene being mutual. Models fabricated for camping and RV use frequently have the option of running (inefficiently) on 12 volt battery power.
Peltier refrigerators [edit]
- Peltier refrigerators are powered by electricity, usually 12 volt DC, but mains-powered wine coolers are available. Peltier refrigerators are inexpensive but inefficient and get progressively more than inefficient with increased cooling event; much of this inefficiency may be related to the temperature differential across the short distance between the "hot" and "cold" sides of the Peltier prison cell. Peltier refrigerators mostly use heat sinks and fans to lower this differential; the only noise produced comes from the fan. Reversing the polarity of the voltage applied to the Peltier cells results in a heating rather than cooling effect.
Other specialized cooling mechanisms may be used for cooling, just have non been applied to domestic or commercial refrigerators.
Magnetic refrigerator [edit]
- Magnetic refrigerators are refrigerators that piece of work on the magnetocaloric consequence. The cooling effect is triggered by placing a metallic alloy in a magnetic field.[24]
- Acoustic refrigerators are refrigerators that use resonant linear reciprocating motors/alternators to generate a sound that is converted to heat and cold using compressed helium gas. The heat is discarded and the common cold is routed to the refrigerator.
Energy efficiency [edit]

A European free energy label for a fridge
In a house without air-conditioning (space heating and/or cooling) refrigerators consumed more energy than any other domicile device.[25] In the early 1990s a competition was held among the major manufacturers to encourage energy efficiency.[26] Current U.s.a. models that are Energy Star qualified utilize fifty% less energy than the average models made in 1974.[27] The most energy-efficient unit fabricated in the US consumes virtually half a kilowatt-hr per day (equivalent to 20 W continuously).[28] But fifty-fifty ordinary units are quite efficient; some smaller units use less than 0.2 kWh per day (equivalent to eight W continuously). Larger units, especially those with big freezers and icemakers, may use as much every bit 4 kW·h per day (equivalent to 170 W continuously). The European union uses a letter of the alphabet-based mandatory energy efficiency rating characterization instead of the Energy Star; thus European union refrigerators at the bespeak of auction are labelled co-ordinate to how energy-efficient they are.
For US refrigerators, the Consortium on Energy Efficiency (CEE) further differentiates between Free energy Star qualified refrigerators. Tier ane refrigerators are those that are 20% to 24.9% more efficient than the Federal minimum standards set by the National Appliance Energy Conservation Act (NAECA). Tier ii are those that are 25% to 29.ix% more efficient. Tier 3 is the highest qualification, for those refrigerators that are at least thirty% more efficient than Federal standards.[29] Virtually 82% of the Energy Star qualified refrigerators are Tier i, with 13% qualifying equally Tier ii, and but 5% at Tier three.[ citation needed ]
Besides the standard style of compressor refrigeration used in normal household refrigerators and freezers, there are technologies such as assimilation refrigeration and magnetic refrigeration. Although these designs by and large apply a much larger amount of energy compared to compressor refrigeration, other qualities such every bit silent operation or the power to apply gas can favor these refrigeration units in pocket-size enclosures, a mobile environment or in environments where unit failure would lead to devastating consequences.[ citation needed ]
Many refrigerators made in the 1930s and 1940s were far more efficient than about that were made subsequently. This is partly attributable to the addition of new features, such as car-defrost, that reduced efficiency. Additionally, after World War 2, refrigerator style became more than important than efficiency. This was peculiarly truthful in the United states of america in the 1970s, when side-past-side models (known as American fridgefreezers outside of the US) with ice dispensers and water chillers became popular. However, the reduction in efficiency also arose partly from reduction in the amount of insulation to cut costs.[ citation needed ]
Today [edit]

Display of modern American-manner / side-by-side refrigerators, available for purchase in a store
Considering of the introduction of new energy efficiency standards, refrigerators made today are much more than efficient than those made in the 1930s; they consume the same amount of energy while being three times equally large.[30] [31]
The efficiency of older refrigerators can exist improved past defrosting (if the unit is manual defrost) and cleaning them regularly, replacing erstwhile and worn door seals with new ones, adjusting the thermostat to accommodate the actual contents (a refrigerator needn't be colder than 4 °C (39 °F) to shop drinks and not-perishable items) and also replacing insulation, where applicable. Some sites recommend cleaning condenser coils every month or so on units with coils on the rear, to add together life to the coils and not suffer an unnoticeable deterioration in efficiency over an extended period, the unit should be able to ventilate or "breathe" with adequate spaces around the front, back, sides and above the unit. If the fridge uses a fan to keep the condenser cool, so this must be cleaned or serviced, at per individual manufactures recommendations.[ commendation needed ]
Auto defrosting [edit]
Frost-free refrigerators or freezers use electrical fans to cool the appropriate compartment.[32] This could be called a "fan forced" fridge, whereas manual defrost units rely on colder air lying at the bottom, versus the warm air at the top to attain adequate cooling. The air is fatigued in through an inlet duct and passed through the evaporator where it is cooled, the air is and so circulated throughout the cabinet via a serial of ducts and vents. Because the air passing the evaporator is supposedly warm and moist, frost begins to form on the evaporator (particularly on a freezer's evaporator). In cheaper and/or older models, a defrost cycle is controlled via a mechanical timer. This timer is set to shut off the compressor and fan and energize a heating element located almost or around the evaporator for about 15 to xxx minutes at every 6 to 12 hours. This melts any frost or ice build up and allows the refrigerator to piece of work usually once more. It is believed that frost free units have a lower tolerance for frost, due to their air-conditioner similar evaporator coils. Therefore, if a door is left open up accidentally (especially the freezer), the defrost organisation may not remove all frost, in this case, the freezer (or refrigerator) must be defrosted.[ commendation needed ]
If the defrosting system melts all the ice before the timed defrosting period ends, and so a pocket-sized device (called a defrost limiter) acts like a thermostat and shuts off the heating element to forbid too big a temperature fluctuation, it also prevents hot blasts of air when the arrangement starts once again, should it terminate defrosting early. On some early on frost-free models, the defrost limiter besides sends a signal to the defrost timer to start the compressor and fan every bit soon as it shuts off the heating chemical element before the timed defrost cycle ends. When the defrost cycle is completed, the compressor and fan are allowed to bike back on.[ citation needed ]
Frost-free refrigerators, including some early on frost gratis refrigerator/freezers that used a cold plate in their fridge section instead of airflow from the freezer department, by and large don't close off their refrigerator fans during defrosting. This allows consumers to leave food in the master refrigerator compartment uncovered, and besides helps keep vegetables moist. This method also helps reduce energy consumption, because the refrigerator is in a higher place freeze point and tin pass the warmer-than-freezing air through the evaporator or common cold plate to assistance the defrosting bicycle.[ citation needed ]
Inverter [edit]

Refrigerator in a rural shop
With the advent of digital inverter compressors, the energy consumption is fifty-fifty farther reduced than a single-speed induction motor compressor, and thus contributes far less in the fashion of greenhouse gases.[33]
The energy consumption of a refrigerator is too dependent on the type of refrigeration being done. For instance, Inverter Refrigerators consume comparatively less energy than a typical not-inverter refrigerator. In an inverter fridge, the compressor is used conditionally on requirement basis. For instance, an inverter refrigerator might use less energy during the winters than it does during the summers. This is considering the compressor works for a shorter time than it does during the summers.[34]
Further, newer models of inverter compressor refrigerators accept in to account diverse external and internal conditions to adjust the compressor speed and thus optimize cooling and energy consumption. Most of them use at least 4 sensors which aid detect variance in external temperature, internal temperature attributable to opening of the refrigerator door or keeping new food inside; humidity and usage patterns. Depending on the sensor inputs, the compressor adjusts its speed. For instance, if door is opened or new nutrient is kept, the sensor detects an increment in temperature inside the motel and signals the compressor to increment its speed till a pre-adamant temperature is attained. After which, the compressor runs at a minimum speed to just maintain the internal temperature. The compressor typically runs between 1200 and 4500 rpm. Inverter compressors not only optimizes cooling only is also superior in terms of immovability and energy efficiency.[ citation needed ] A device consumes maximum energy and undergoes maximum habiliment and tear when it switches itself on. As an inverter compressor never switches itself off and instead runs on varying speed, it minimizes wear and tear and energy usage. LG played a significant function in improving inverter compressors as we know information technology by reducing the friction points in the compressor and thus introducing Linear Inverter Compressors. Conventionally, all domestic refrigerators apply a reciprocating drive which is connected to the piston. Simply in a linear inverter compressor, the piston which is a permanent magnet is suspended between two electromagnets. The AC changes the magnetic poles of the electromagnet, which results in the push button and pull that compresses the refrigerant. LG claims that this helps reduce energy consumption by 32% and noise past 25% compared to their conventional compressors.
Form cistron [edit]
The phycial design of refrigerators besides plays a large part in its free energy efficiency. The virtually efficient is the chest-style freezer, equally its top-opening design minimizes convection when opening the doors, reducing the corporeality of warm moist air entering the freezer. On the other hand, in-door ice dispensers cause more than estrus leakage, contributing to an increment in free energy consumption.[35]
Effect on lifestyle [edit]
The fridge allows households to keep nutrient fresh for longer than before. The most notable improvement is for meat and other highly perishable wares, which needed to be refined to gain anything resembling shelf life.[ commendation needed ] (On the other hand, refrigerators and freezers tin can too exist stocked with processed, quick-cook foods that are less salubrious.) Refrigeration in transit makes information technology possible to enjoy food from distant places.
Dairy products, meats, fish, poultry and vegetables can be kept refrigerated in the aforementioned infinite within the kitchen (although raw meat should exist kept separate from other food for reasons of hygiene).
Freezers allow people to purchase food in bulk and eat it at leisure, and majority purchases relieve coin. Ice cream, a pop commodity of the 20th century, could previously just be obtained past traveling to where the production was made and eating it on the spot. Now it is a mutual nutrient item. Ice on demand not only adds to the enjoyment of cold drinks, simply is useful for offset-aid, and for cold packs that can exist kept frozen for picnics or in instance of emergency.
Temperature zones and ratings [edit]
Residential units [edit]
The chapters of a fridge is measured in either liters or cubic anxiety. Typically the volume of a combined refrigerator-freezer is separate with one/3rds to 1/quaternary of the volume allocated to the freezer although these values are highly variable.
Temperature settings for fridge and freezer compartments are frequently given arbitrary numbers past manufacturers (for example, ane through 9, warmest to coldest), but generally 3 to v °C (37 to 41 °F)[ane] is platonic for the fridge compartment and −18 °C (0 °F) for the freezer. Some refrigerators must be within certain external temperature parameters to run properly. This can be an issue when placing units in an unfinished expanse, such every bit a garage.
Some refrigerators are now divided into four zones to shop dissimilar types of food:
- −18 °C (0 °F) (freezer)
- 0 °C (32 °F) (meat zone)
- five °C (41 °F) (cooling zone)
- 10 °C (l °F) (crisper)
European freezers, and refrigerators with a freezer compartment, have a four star rating organisation to course freezers.[36]
- [∗] : min temperature = −half dozen °C (21 °F).
-
-
- Maximum storage time for (pre-frozen) food is 1 week
-
- [∗∗] : min temperature = −12 °C (ten °F).
-
-
- Maximum storage fourth dimension for (pre-frozen) nutrient is ane month
-
- [∗∗∗] : min temperature = −18 °C (0 °F).
-
-
- Maximum storage time for (pre-frozen) food is between 3 and 12 months
- depending on blazon (meat, vegetables, fish, etc.)
- Maximum storage time for (pre-frozen) food is between 3 and 12 months
-
- [∗∗∗∗] : min temperature = −18 °C (0 °F).
-
-
- Maximum storage fourth dimension for pre-frozen or frozen-from-fresh food is between 3 and 12 months
-
Although both the three and four star ratings specify the same storage times and aforementioned minimum temperature of −18 °C (0 °F), only a 4 star freezer is intended for freezing fresh food, and may include a "fast freeze" role (runs the compressor continually, down to as low every bit −26 °C (−15 °F)) to facilitate this. Iii (or fewer) stars are used for frozen food compartments that are only suitable for storing frozen food; introducing fresh food into such a compartment is likely to result in unacceptable temperature rises. This difference in categorization is shown in the design of the four-star logo, where the "standard" three stars are displayed in a box using "positive" colours, denoting the same normal operation as a 3-star freezer, and the 4th star showing the additional fresh food/fast freeze office is prefixed to the box in "negative" colours or with other distinct formatting.[ citation needed ]
Almost European refrigerators include a moist cold fridge section (which does crave (automatic) defrosting at irregular intervals) and a (rarely frost free) freezer section.
Commercial refrigeration temperatures [edit]
(from warmest to coolest)
- Refrigerators
- ii to three °C (35 to 38 °F), and not greater than maximum refrigerator temperature at 5 °C (41 °F)
- Freezer, Achieve-in
- −23 to −15 °C (−ten to +five °F)
- Freezer, Walk-in
- −23 to −18 °C (−10 to 0 °F)
- Freezer, Ice Cream
- −29 to −23 °C (−20 to −x °F)
Disposal [edit]

1941 Ad for Servel Electrolux Gas Refrigerator (Absorption),[37] designed by Norman Bel Geddes.[38] [39] [40] In 1998, CPSC warned that one-time units withal in utilise could be mortiferous, and offered a $100 reward plus disposal costs to consumers who properly disposed of their one-time Servels.[41]
An increasingly important environmental concern is the disposal of one-time refrigerators—initially because freon coolant amercement the ozone layer—simply as older generation refrigerators wearable out, the destruction of Chlorofluorocarbon-bearing insulation also causes business. Modernistic refrigerators usually utilise a refrigerant called HFC-134a (one,1,1,2-Tetrafluoroethane), which does not deplete the ozone layer, unlike Freon. A R-134a is now condign very uncommon in Europe. Newer refrigerants are being used instead. The primary refrigerant now used is R-600a, or isobutane which has a smaller effect on the atmosphere if released. There have been reports of refrigerators exploding if the refrigerant leaks isobutane in the presence of a spark. If the coolant leaks into the refrigerator, at times when the door is not beingness opened (such as overnight) the concentration of coolant in the air within the fridge can build upward to form an explosive mixture that tin exist ignited either by a spark from the thermostat or when the light comes on as the door is opened, resulting in documented cases of serious belongings damage and injury or even death from the resulting explosion.[42]
Disposal of discarded refrigerators is regulated, oft mandating the removal of doors for safety reasons. Children playing hide-and-seek have been asphyxiated while hiding inside discarded refrigerators, particularly older models with latching doors, in a phenomenon called refrigerator death. Since 2 August 1956, under U.S. federal law, refrigerator doors are no longer permitted to latch and they can exist opened from the inside.[43] Modern units use a magnetic door gasket that holds the door sealed only allows it to be pushed open up from the inside.[44] This gasket was invented, developed and manufactured by Max Baermann (1903–1984) of Bergisch Gladbach/Germany.[45] [46]
Regarding full life-bicycle costs, many governments offer incentives to encourage recycling of old refrigerators. I example is the Phoenix fridge plan launched in Australia. This government incentive picked upwards old refrigerators, paying their owners for "donating" the fridge. The refrigerator was and then refurbished, with new door seals, a thorough cleaning and the removal of items, such every bit the embrace that is strapped to the back of many older units. The resulting refrigerators, now over x% more efficient, were so distributed to low income families.[ citation needed ]
Gallery [edit]

-

McCray pre-electrical home refrigerator ad from 1905; this company, founded in 1887, is still in business
-

General Electric "Monitor-Top" fridge, still in use, June 2007
-

Frigidaire Imperial "Frost Proof" model FPI-16BC-63, top refrigerator/bottom freezer with brushed chrome door finish made past General Motors Canada in 1963
-

A side-by-side fridge-freezer with an icemaker (2011)
Run into also [edit]
- Auto-defrost
- Common cold chain
- Continuous freezers
- Home automation
- Ice cream maker
- Water ice famine
- Internet fridge
- KECO Industries, Inc. v. United States
- Kimchi refrigerator
- List of home appliances
- Pot-in-pot refrigerator
- Refrigerator expiry
- Fridge magnet
- Solar-powered refrigerator
- Star rating
- H2o dispenser
- Wine cellar
References [edit]
- ^ a b . Go on your fridge-freezer clean and water ice-gratis. BBC. xxx April 2008
- ^ . Are You Storing Nutrient Safely? FDA. 9 February 2022
- ^ "Yakhchāls, Āb Anbārs, & Air current Catchers — Passive Cooling & Refrigeration Technologies Of Greater Iran (Persia)". TandfOnline. 28 April 2022. Retrieved 22 January 2022.
- ^ Ebrahimi, Ali; Shayegani, Aida; Zarandi, Mahnaz Mahmoudi (2021). "Thermal Performance of Sustainable Element in Moayedi Icehouse in Iran". International Periodical of Architectural Heritage. 15 (5): 740–756. doi:10.1080/15583058.2019.1645243. S2CID 202094054. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ Venetum Britannicum, 1676, London, p. 176 in the 1678 edition.
- ^ Arora, Ramesh Chandra (30 March 2022). "Mechanical vapour compression refrigeration". Refrigeration and Air conditioning. New Delhi, Bharat: PHI Learning. p. three. ISBN978-81-203-3915-half dozen.
- ^ Burstall, Aubrey F. (1965). A History of Mechanical Engineering. The MIT Printing. ISBN0-262-52001-X.
- ^ The states 8080A, John Gorrie, "Improved process for the artificial production of ice", issued 1851-05-06
- ^ "Fridge vacuum dehydration unit". Vacuum. 28 (2): 81. Feb 1978. doi:10.1016/s0042-207x(78)80528-4. ISSN 0042-207X.
- ^ U.s. 1126605, Fred West. Wolf, "Refrigerating apparatus", issued 1915-01-26
- ^ Dennis R. Heldman (29 August 2003). Encyclopedia of Agricultural, Food, and Biological Technology (Print). CRC Press. p. 350. ISBN978-0-8247-0938-nine. Archived from the original on v May 2022.
- ^ "DOMELRE Offset Electric Refrigerator | ashrae.org". www.ashrae.org . Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ^ "Air Conditioning and Refrigeration History - part 3 - Greatest Technology Achievements of the Twentieth Century". world wide web.greatachievements.org . Retrieved 2 Baronial 2022.
- ^ "G.E. Monitor Top Refrigerator". www.industrialdesignhistory.com . Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ Lobocki, Neil (4 October 2022). "The General Electric Monitor Acme Fridge". Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "GE Monitor-Meridian Fridge - Albany Establish of History and Art". www.albanyinstitute.org.
- ^ "The History of Household Wonders: History of the Refrigerator". History.com. A&East Goggle box Networks. 2006. Archived from the original on 26 March 2008.
- ^ "Freezing and nutrient safe". USDA. Archived from the original on 18 September 2022. Retrieved half-dozen August 2022.
- ^ "Ad". The Australian Women'southward Weekly. Commonwealth of australia. 19 September 1973. p. 26. Retrieved 13 Jan 2022 – via Trove.
- ^ "What is Dual-Cooling Technology?". www.sears.com.
- ^ James, Stephen J. (2003). "Developments in domestic refrigeration and consumer attitudes" (PDF). Bulletin of the IIR. 5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 March 2009.
- ^ Refrigerator – Adjusting Temperature Controls. geappliances.com
- ^
- ^ "Towards the magnetic refrigerator" Archived 7 Dec 2008 at the Wayback Automobile. Physorg. 21 April 2006
- ^ "Which UK – Saving Energy". Which United kingdom. Archived from the original on 10 Nov 2022. Retrieved ten November 2022.
- ^ Feist, J. Due west.; Farhang, R.; Erickson, J.; Stergakos, East. (1994). "Super Efficient Refrigerators: The Golden Carrot from Concept to Reality" (PDF). Proceedings of the ACEEE. 3: three.67–3.76. Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 September 2022.
- ^ "Refrigerators & Freezers". Energy Star. Archived from the original on seven February 2006.
- ^ Itakura, Kosuke. Sun Frost – The World'southward Most Efficient Refrigerators. Humboldt.edu
- ^ "High-efficiency specifications for REFRIGERATORS" (PDF). Consortium for Energy Efficiency. January 2007. Archived (PDF) from the original on 15 January 2022.
- ^ "Successes of Energy Efficiency: The United States and California National Trust" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 25 Feb 2022.
- ^ Calwell, Chris & Reeder, Travis (2001). "Out With the Old, In With the New" (PDF). Natural Resources Defence force Quango. Archived (PDF) from the original on 8 June 2022.
- ^ Kakaç, Sadik; Avelino, M. R.; Smirnov, H. F. (vi December 2022). Low Temperature and Cryogenic Refrigeration. Springer Scientific discipline & Business Media. ISBN9789401000994.
- ^ "How the Digital Inverter Compressor Has Transformed the Mod Refrigerator". news.samsung.com . Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "How to Adjust the Temperature in Your Fridge During the Winter & the Summer". homeguides.sfgate.com . Retrieved 8 May 2022.
- ^ Technology Connections (vii April 2022). "Chest Freezers; What they tell u.s. about designing for X". YouTube.
- ^ Commission Regulation (European union) 2022/2019 of 1 October 2022 laying down ecodesign requirements for refrigerating appliances pursuant to Directive 2009/125/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council and repealing Committee Regulation (EC) No 643/2009 (Text with EEA relevance.), v December 2022, retrieved 21 October 2022
- ^ Lobocki, Neil (4 Oct 2022). "The First Absorption Fridge". Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ United states of america 95817S, Norman Bel Geddes, "Design for a refrigerator cabinet", issued 1935-06-04
- ^ US 2127212A, Norman Bel Geddes, "Refrigerator", published 1935-07-24, issued 1938-08-16
- ^ "Norman Bel Geddes Database". norman.hrc.utexas.edu . Retrieved 25 Jan 2022.
- ^ "CPSC, Warns That Quondam Servel Gas Refrigerators All the same In Apply Tin Be Deadly". U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission. 19 May 2022. Retrieved 25 January 2022.
- ^ "Tragic helpmate-to-be's fridge-freezer exploded and 'turned into a Bunsen burner'". Daily Mirror. 12 Nov 2022. Archived from the original on 5 August 2022. Retrieved 14 June 2022. Daily Mirror November 2022
- ^ PART 1750—STANDARD FOR DEVICES TO Let THE OPENING OF HOUSEHOLD REFRIGERATOR DOORS FROM THE Within :: PART 1750-STANDARD FOR DEVICES TO PERMIT THE OPENING OF HOUSEHOLD REFRI. Law.justia.com. Retrieved on 26 August 2022.
- ^ Adams, Cecil (2005). "Is it impossible to open a fridge door from the inside?". Archived from the original on 7 July 2006. Retrieved 31 August 2006.
- ^ Max Baermann GMBH. "Flexible Magnetic Strips". Archived from the original on 28 April 2022. Retrieved 20 June 2022.
- ^ US 2959832, Max Baermann, "Flexible or resilient permanent magnets", issued 1960-11-15
Further reading [edit]
- Rees, Jonathan. Refrigeration Nation: A History of Water ice, Appliances, and Enterprise in America (Johns Hopkins University Press; 2022) 256 pages
- Refrigerators and food preservation in foreign countries. United States Agency of Statistics, Department of State. 1890.
External links [edit]
- U.South. Patent 1,126,605 Refrigerating apparatus
- U.S. Patent 1,222,170 Refrigerating apparatus
- The History of the Fridge and Freezers
- Refrigerators, Canada Scientific discipline and Technology Museum
- "Walking refrigerator, comes when you call it". Engadget . Retrieved 8 March 2022.
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Refrigerator
Posted by: rousselhigend1992.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Should You Repair A 20 Year Old Refrigerator"
Post a Comment